Private jet ownership has long been associated with immense wealth, exclusivity, and business efficiency. As the global economy grows and the ultra-high-net-worth population expands, the number of private jets circulating worldwide has steadily increased. However, within this elite sphere, the ownership of multiple private jets—specifically, owning 10 or more—remains a rare and intriguing phenomenon that raises questions about patterns of wealth, regulatory oversight, and the environmental impact of such luxury travel.
Understanding who owns 10 private jets provides insight not only into the lifestyles of the ultra-wealthy but also into the evolving dynamics of the private aviation industry. Multi-jet ownership often reflects the operational needs of global businesses, governmental functions, or the personal preferences of billionaires seeking flexibility, privacy, and status.
This article investigates the ownership of 10 or more private jets by individuals, corporations, and governments worldwide. Drawing upon data from aviation regulatory authorities, industry reports, and public registries, the article aims to present a factual, balanced overview of this exclusive group. It further explores related regulatory frameworks, industry trends, and the broader implications of concentrated private jet ownership in the modern era.
Who Owns 10 Private Jets?
Introduction to Multi-Jet Ownership
Owning 10 or more private jets places an individual or entity in an exceptionally exclusive category within the private aviation world. Such ownership is a reflection not only of substantial wealth but also of complex operational, business, or governmental needs. While the global private jet fleet numbers around 22,000 aircraft, only a tiny fraction of owners possess multiple jets, making multi-jet ownership a rare and significant phenomenon. Understanding who owns 10 private jets provides insights into luxury, business efficiency, and regulatory challenges faced by this elite group.
Roman Abramovich
Roman Abramovich, the Russian billionaire and former Chelsea FC owner, reportedly owns a fleet exceeding 10 private jets. His collection includes Gulfstream G650s, Boeing Business Jets, and other long-range aircraft, often registered through corporate entities to maintain privacy and operational flexibility. These jets enable rapid travel across Abramovich’s numerous global holdings.

Sheikh Mansour bin Zayed Al Nahyan
Sheikh Mansour bin Zayed Al Nahyan, a member of Abu Dhabi’s ruling family, commands a luxury fleet exceeding 10 jets. These aircraft serve both personal and governmental functions, offering versatility across a broad spectrum of missions and destinations.

Prince Alwaleed Bin Talal
Prince Alwaleed Bin Talal, the Saudi investor, is known for a fleet that often numbers 10 or more private jets, supporting his extensive business ventures worldwide. His ownership underscores the blend of prestige and practicality that multi-jet ownership represents.

Michael Bloomberg
In the United States, Michael Bloomberg maintains a sizable fleet split between personal use and corporate operations. This arrangement supports his vast global business interests and philanthropic activities by facilitating seamless international travel.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk has historically owned several private jets concurrently, sometimes nearing or exceeding 10 aircraft. His fleet has evolved in response to the demands of managing multiple companies, including Tesla and SpaceX.
Corporate Ownership of Multiple Jets
Multi-jet ownership is also prevalent among corporations. For example, NetJets, a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway, operates over 700 private jets globally, providing fractional ownership and charter services. Such corporate fleets highlight a shift from sole ownership to shared models, expanding access to private aviation while maintaining fleet efficiency.
Other multinational companies maintain fleets of multiple jets for executive travel and operational needs. These corporate fleets often include various aircraft types tailored to diverse mission profiles and geographic coverage.
Government and Institutional Multi-Jet Ownership
Governments maintain extensive private jet fleets for official, diplomatic, and defense purposes. The United States operates a number of jets, including the well-known Air Force One, while countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia maintain similar multi-jet fleets for official use. These government-owned fleets are mission-driven, emphasizing security, diplomacy, and state functions rather than personal luxury.
Ownership Structures and Transparency Challenges
Multi-jet ownership frequently involves complex legal arrangements such as trusts, shell companies, and nominee owners. These structures are used to manage operational efficiency, optimize taxation, and ensure privacy. Consequently, identifying the beneficial owners—the individuals or entities with ultimate control—is often difficult.
Aviation registries provide records of registered owners but rarely disclose beneficial ownership. This lack of transparency poses challenges for regulatory bodies aiming to enforce compliance and monitor ownership concentration. Recent regulations have sought to improve disclosure, but gaps remain.
Historical Evolution of Multi-Jet Ownership
Owning multiple private jets emerged as a practical and prestigious option with advances in aviation technology and the globalization of business. While once owning a single jet was exclusive, today’s multi-jet owners leverage these assets for global reach and strategic mobility.
The rise of fractional ownership and changing economic and environmental concerns are now influencing how multi-jet ownership evolves, introducing alternatives that balance exclusivity with sustainability.
Global Private Jet Ownership Overview
Private jet ownership is a global phenomenon shaped by regional economic conditions, cultural preferences, and regulatory environments. While the majority of private jets operate in North America and Europe, significant growth has been observed in the Middle East, Asia-Pacific, and emerging markets.
Regional Trends in Ownership
North America remains the largest market for private jets, accounting for a substantial portion of global private aircraft. The United States, in particular, hosts the highest number of private jets and multi-jet owners, facilitated by a well-established aviation infrastructure and a high concentration of ultra-wealthy individuals and corporations.
In Europe, ownership is more diversified across countries such as the United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Switzerland. European owners often face stricter regulatory and environmental frameworks, influencing ownership patterns and fleet management strategies.
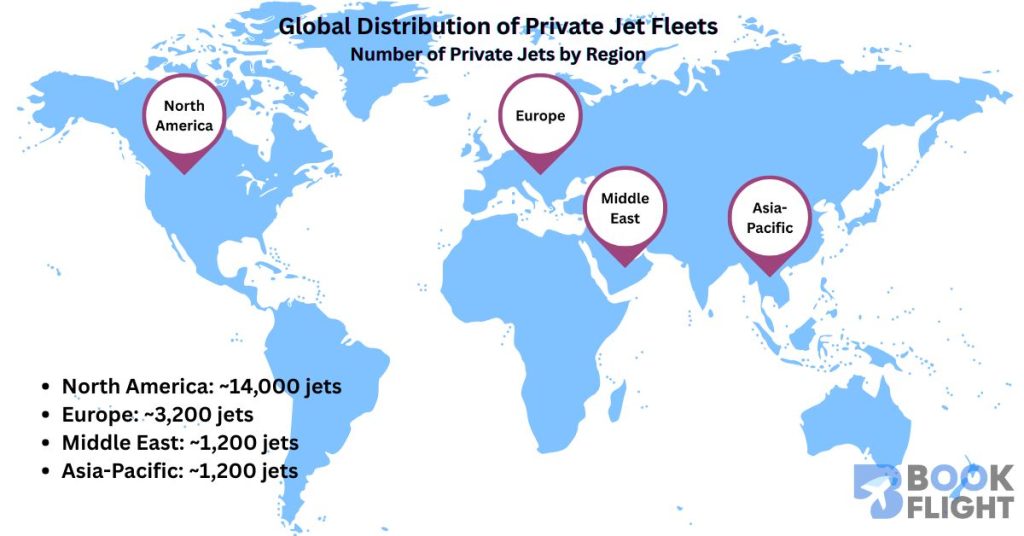
The Middle East is notable for its wealthy ruling families and business magnates who own and operate sizable private jet fleets. Countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are key hubs for multi-jet ownership, reflecting both personal luxury and government use.
Asia-Pacific is an emerging market, with growing numbers of private jets owned by billionaires and corporations in China, India, and Southeast Asia. While individual multi-jet ownership remains less common compared to the West, companies like JetSetGo in India are innovating with fractional ownership models, expanding access to private aviation.
In addition to luxury and business use, private jets also serve critical roles in emergency medical transport, with specialized air ambulance services gaining prominence in countries like India.
Types of Owners
Private jets are owned by a variety of stakeholders including:
- Ultra-high-net-worth individuals (UHNWIs): Individuals owning multiple jets for personal convenience, privacy, and business efficiency.
- Corporations: Companies maintain fleets to facilitate executive travel, often operating under corporate ownership to optimize costs and logistics.
- Governments: State-owned jets serve official functions, diplomatic missions, and military transport.
- Charter companies and fractional ownership firms: These entities own fleets that are shared by multiple owners or customers, reducing individual ownership burdens.
Market Size and Growth
According to industry reports, The global private jet fleet numbers over 22,000 aircraft, with a significant portion concentrated among a small percentage of owners who hold multiple jets.The market has seen steady growth driven by rising global wealth, increased demand for flexibility, and evolving business travel needs.
Family offices and investment groups are increasingly involved in private aviation, acquiring fleets for diversified business and lifestyle purposes. This concentration highlights the importance of understanding ownership dynamics, especially among those holding 10 or more jets.
Regulatory Framework and Ownership Transparency
Effective regulation and transparent ownership disclosure are essential components of the private aviation industry. Given the high value and sensitive nature of private jets, regulatory authorities worldwide have established frameworks to govern aircraft registration, ownership reporting, and operational compliance. This section explores the key regulatory bodies involved, the requirements for ownership disclosure, recent policy updates, and the ongoing challenges in achieving transparency. It also discusses the delicate balance regulators must maintain between protecting individual privacy and ensuring public accountability.
Aviation Regulatory Authorities
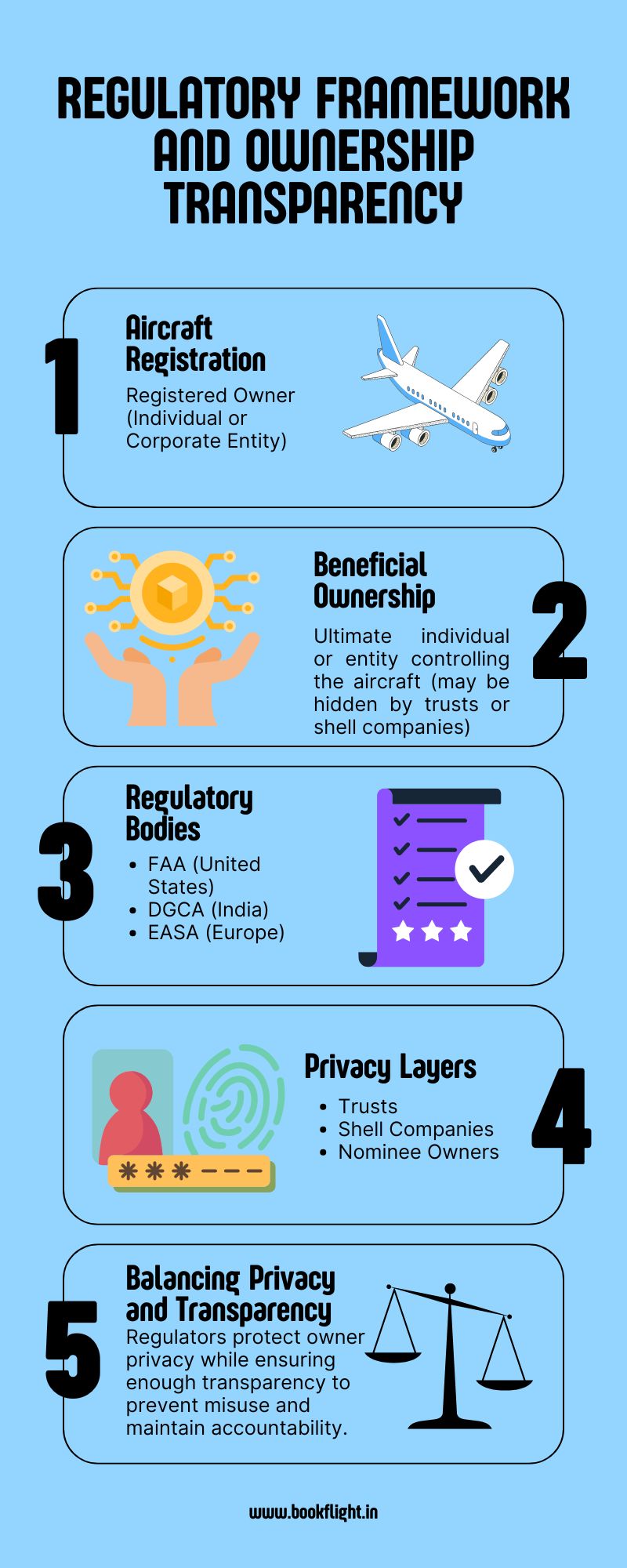
The ownership and operation of private jets are overseen by national and regional aviation authorities. Key regulators include the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) in India, and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) in Europe. These agencies are responsible for aircraft registration, airworthiness certification, and enforcement of operational standards that impact private jet ownership and usage.
Ownership Registration and Disclosure Requirements
Private jets must be registered with the relevant aviation authority of the country where they operate. Registration documents generally list the owner’s name and aircraft specifications, but the transparency of beneficial ownership varies significantly by jurisdiction. In many cases, the true owner of a private jet—especially when an individual owns multiple aircraft—is obscured through trusts, shell companies, or nominee arrangements, complicating efforts to track multi-jet ownership.
Recent Regulatory Updates
In recent years, regulatory bodies have increased efforts to enhance ownership transparency, particularly to counter money laundering, tax evasion, and misuse of private aircraft. The FAA, for instance, has tightened disclosure requirements, requiring more detailed information about beneficial ownership. The European Union has enacted anti-money laundering directives mandating greater transparency around beneficial ownership of aviation assets. Meanwhile, India’s DGCA maintains registration protocols but currently lacks extensive public disclosure requirements, making it difficult to ascertain the ownership of multiple jets in some cases.
Challenges in Ownership Transparency
The question “Who owns 10 private jets?” is difficult to answer conclusively due to the opaque nature of many ownership structures. The use of shell companies, offshore trusts, and nominee registrants allows owners to shield their identities from public records and regulatory scrutiny. These complexities challenge regulators and researchers alike in identifying true multi-jet owners and assessing the scale of private jet fleets held by individuals.
Balancing Privacy and Public Interest
While transparency is vital to ensure regulatory compliance and prevent illicit activities, many private jet owners argue that privacy is necessary for personal security and competitive business reasons. Aviation regulators face the ongoing task of balancing these competing interests: enforcing adequate ownership transparency to promote accountability without unduly infringing on privacy rights.
Industry News and Policy Changes Affecting Multi-Jet Owners
As private jet ownership continues to evolve, industry news and shifting policy landscapes significantly influence the behavior and decisions of multi-jet owners. Economic factors, environmental regulations, taxation, and emerging ownership models all play a role in shaping how private jets are acquired and operated. This section reviews recent developments that affect individuals and entities owning 10 or more private jets, highlighting the dynamic nature of the private aviation sector.
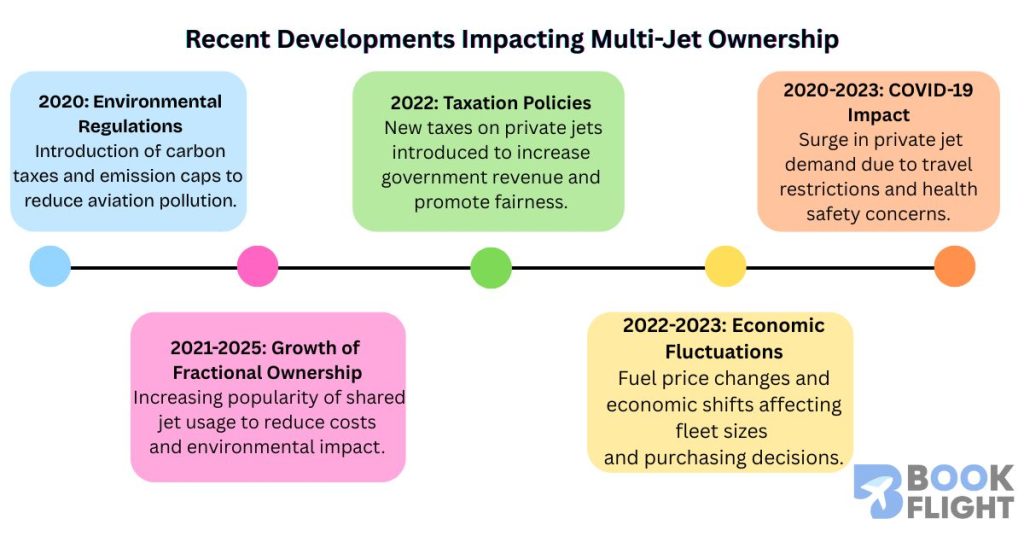
Environmental Regulations and Carbon Emissions
The growing global emphasis on sustainability has led to stricter environmental policies targeting aviation emissions. Governments and international bodies are introducing carbon taxes, emission caps, and operational restrictions aimed at reducing the environmental impact of private jets. These measures increase operating costs and encourage multi-jet owners to adopt greener technologies or alternative usage models.
Growth of Fractional Ownership and Shared Jet Models
To address cost and sustainability challenges, fractional ownership and shared charter services have become more prevalent. These models allow multiple individuals or companies to share access to a jet, providing flexibility and cost savings. Such trends influence the traditional concept of owning multiple jets, as they offer viable alternatives that reduce the need for sole ownership of large fleets.
Economic Factors Influencing Ownership
Private jet ownership patterns are sensitive to global economic conditions. Fluctuations in fuel prices, economic growth rates, and wealth distribution impact the ability and willingness of owners to acquire and maintain multiple jets. During economic slowdowns, fleet reductions and delayed acquisitions are common, while periods of prosperity tend to see fleet expansion.
Taxation Policies and Luxury Asset Regulations
Increasing scrutiny of luxury assets has prompted governments to revisit tax regimes affecting private jets. New taxes on ownership, usage, and acquisition costs are designed to address revenue needs and social equity concerns. These fiscal policies influence multi-jet owners by altering the financial calculus of fleet ownership.
Industry Perspectives and the Impact of COVID-19
Industry groups such as the National Business Aviation Association (NBAA) and the General Aviation Manufacturers Association (GAMA) play important roles in shaping policy discussions. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated demand for private jet travel, highlighting its role in health security and business continuity. This surge has influenced fleet dynamics and ownership patterns, at least in the short term.
Implications of Multi-Jet Ownership on Aviation and Society
Economic Impact
The ownership of multiple private jets generates significant economic activity. It supports jobs in aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, airport operations, and various service industries. Multi-jet owners contribute to the growth of business aviation sectors worldwide, fostering innovation and infrastructure development.
Environmental Concerns
Private jets have a disproportionately high carbon footprint compared to commercial flights due to their size and frequency of use. The rise in multi-jet ownership raises concerns about environmental sustainability and climate change. Regulators and industry stakeholders are increasingly focused on mitigating these impacts through emissions regulations and promoting cleaner technologies.
Social and Ethical Considerations
The concentration of private jet ownership among the ultra-wealthy highlights issues of wealth inequality and social justice. The visible use of multiple private jets can intensify public debates about economic disparity and the ethical implications of luxury consumption, especially amid global environmental and social challenges.
Policy and Regulatory Implications
Policymakers face the challenge of balancing the economic benefits of private aviation with environmental sustainability and social equity. Regulations targeting emissions, taxation of luxury assets, and transparency in ownership are central to addressing these concerns, aiming to promote responsible ownership and use of private jets.
Conclusion
The question “Who owns 10 private jets?” highlights an exclusive segment of the private aviation world, dominated by ultra-wealthy individuals, corporations, and governments. Ownership of multiple private jets reflects complex motivations—ranging from operational efficiency to status—and is influenced by evolving regulatory, economic, and environmental factors.
Transparency in ownership remains a challenge due to privacy protections and complex corporate structures, but regulatory efforts worldwide are increasingly aimed at enhancing accountability. The private aviation industry continues to adapt through fractional ownership models and sustainability initiatives, balancing luxury with growing environmental concerns.
Understanding multi-jet ownership provides valuable insights into the dynamics of wealth, regulatory policy, and global aviation trends. As policies and technologies evolve, the future of multi-jet ownership will likely be shaped by ongoing efforts to harmonize operational needs with social responsibility and transparency.
Ready to Take Off into the World of Private Jets?
Dive deeper into the thrilling universe of luxury aviation — from blazing speeds to jaw-dropping jet collections of the ultra-wealthy. Explore insider secrets, discover the best jets, and unlock the sky’s elite lifestyle at BookFlight. Your first-class journey starts here. Why just fly, when you can soar?












