The private aviation industry has experienced robust growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand for personalized, flexible, and secure travel solutions among high-net-worth individuals and corporations. As luxury travel options expand, safety remains a paramount concern for buyers, operators, and flight departments. The stakes are high — Selecting a private jet with superior safety credentials is not merely a matter of comfort but a strategic business decision that protects valuable assets and personnel, including hangar and storage locations.
This article explores the pivotal question: What is the safest private jet in the world? By analyzing industry data, safety records, and technological advancements, we aim to provide decision-makers with a comprehensive and objective overview. Understanding which private jets deliver the highest safety standards is crucial for mitigating operational risks and ensuring peace of mind in luxury travel, including air ambulance capabilities.
From regulatory frameworks to cutting-edge avionics and structural innovations, safety in private aviation is a multi-faceted discipline. Through this analysis, readers will gain actionable insights supported by data and expert evaluations, helping them make well-informed investments aligned with their strategic priorities.
What is the Safest Private Jet in the World? — Data-Driven Analysis and Identification
When assessing what is the safest private jet in the world, it is essential to apply a multi-dimensional safety framework. For an overview of different types of private jets, see our detailed guide. Safety evaluation in private aviation involves scrutinizing accident and incident data, aircraft engineering and structural robustness, avionics and automation capabilities, pilot training standards, and operational maintenance protocols. Regulatory oversight by authorities such as the FAA (Federal Aviation Administration), EASA (European Union Aviation Safety Agency), and ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) further informs safety benchmarks.
Defining Safety Metrics in Private Aviation
Critical safety metrics include:
- Accident and Incident Rates: Historical safety records broken down by jet model and manufacturer, using verified data from FAA, NTSB, and EASA.
- Safety Systems and Redundancy: Integration of advanced avionics such as Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS), Traffic Collision Avoidance Systems (TCAS), autopilot sophistication, and fail-safe redundancies in flight-critical systems.
- Structural Integrity: The use of advanced materials (composites, alloys), design factors enhancing crash survivability, and resilience against operational stress.
- Operational Safety: Pilot qualification standards, recurrent training rigor, and adherence to safety management systems (SMS).
- Maintenance Practices: Utilization of predictive diagnostics and real-time monitoring to preempt failures.
Comparative Safety Performance of Leading Private Jets
Industry data covering the last 10 to 15 years identify several private jets that set the benchmark for safety in the market:
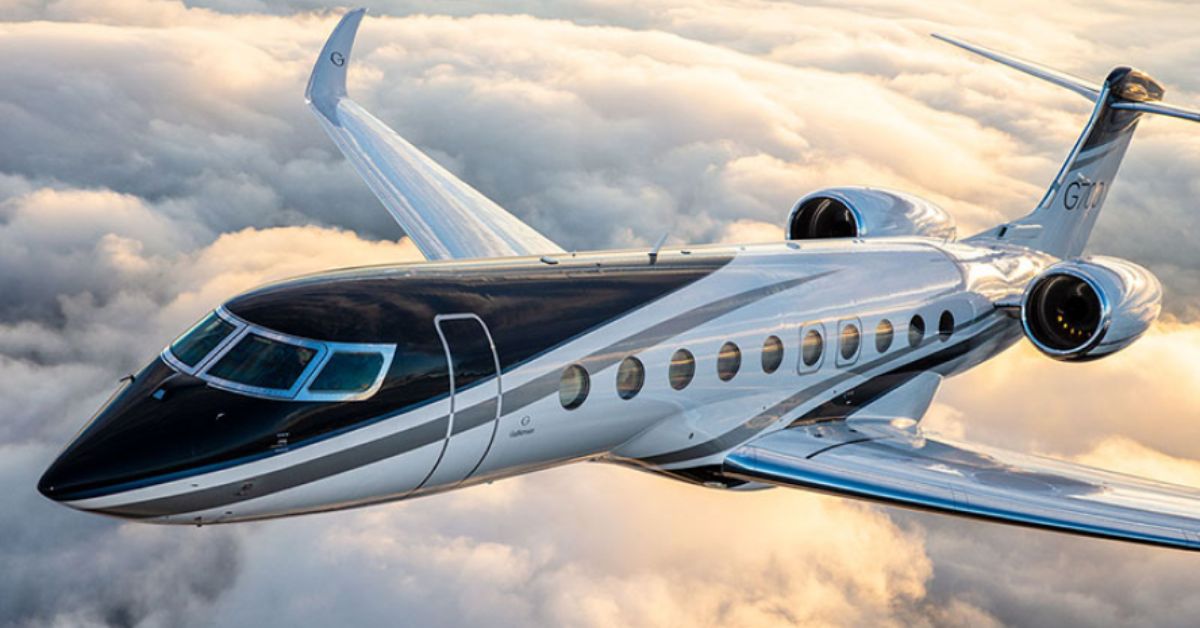
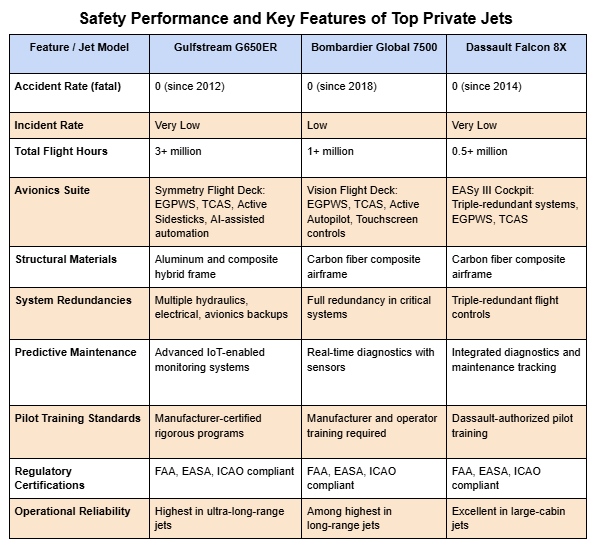
- Gulfstream G650ER: This ultra-long-range business jet exhibits an unparalleled safety record, with zero fatal accidents reported since its launch in 2012. It features the Symmetry Flight Deck with advanced automation, active control sidesticks, and multiple redundancies that reduce pilot workload and human error. With over 3 million flight hours logged, it remains a leader in operational safety.
- Bombardier Global 7500: Incorporating advanced avionics and robust safety certifications, the Global 7500 maintains a minimal incident history. Its composite-heavy airframe and sophisticated onboard systems provide enhanced structural integrity and real-time diagnostics.
- Dassault Falcon 8X: Renowned for its structural robustness and composite airframe, the Falcon 8X integrates triple-redundant flight control systems and advanced de-icing technology, ensuring superior operational safety. Its safety record is consistently strong, with very low incident rates.
- Embraer Praetor 600: A newer entrant emphasizing state-of-the-art avionics and predictive maintenance, the Praetor 600 quickly gains recognition for operational reliability and comprehensive safety protocols.
- Cessna Citation Longitude: While it offers solid safety features and reliable performance, the Citation Longitude trails its competitors in some advanced automation and range capabilities.
In-Depth Safety Feature Breakdown
- Avionics and Flight Automation: Leading jets use EGPWS to warn pilots of terrain proximity and TCAS to prevent mid-air collisions. Gulfstream’s G650ER cockpit boasts real-time systems monitoring and AI-assisted flight controls.
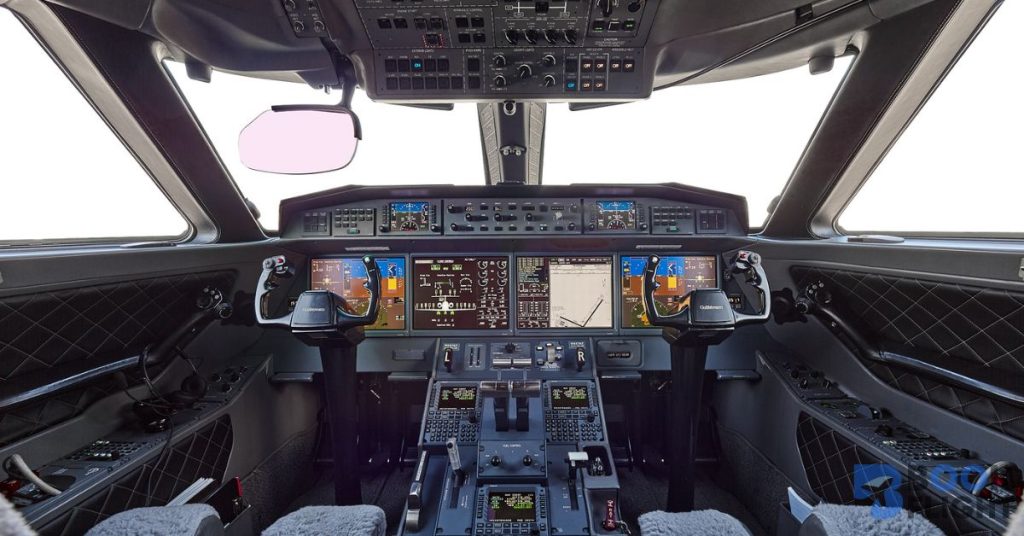

- Structural Design: Carbon-fiber composites, as employed by Dassault Falcon 8X and Bombardier Global 7500, provide enhanced durability and reduce fatigue risk. These materials contribute to survivability and reduce maintenance intervals.
- Redundancy Systems: Multiple backup systems for hydraulics, avionics, and electrical components ensure safety despite system failures, a critical design element in all top-tier jets.
- Maintenance Innovation: Real-time IoT sensors on critical components enable predictive maintenance, reducing the likelihood of in-flight mechanical failures.
Expert Industry Rankings and Consensus
Leading aviation safety consultants and corporate flight departments consistently rank the Gulfstream G650ER as the safest private jet worldwide. Its impeccable accident-free record, comprehensive safety systems, and extensive operator training programs underpin this position. The G650ER’s operational reliability and safety certifications have earned numerous industry awards and set the standard in the ultra-long-range jet category.
The Safest Private Jet in the World
Synthesizing data, expert analyses, and safety performance, the Gulfstream G650ER emerges as the unequivocal safest private jet currently in operation. Its unmatched combination of zero fatal accidents, cutting-edge avionics, advanced structural design, and stringent operational protocols distinguish it as the industry’s gold standard for safety. Business leaders and discerning operators prioritizing passenger protection and operational reliability find the G650ER offers the best balance of safety, performance, and luxury.
Safety Technologies and Innovations Shaping Private Jet Safety
The private aviation industry continually evolves through technological advancements aimed at reducing risks and enhancing passenger safety. Understanding these innovations is vital when assessing what is the safest private jet in the world, as cutting-edge safety technologies are a primary differentiator among top-tier aircraft.
Advanced Avionics Systems
Modern private jets incorporate sophisticated avionics suites that drastically improve situational awareness and flight safety. Key systems include:
- Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS): Provides real-time alerts to pilots about terrain proximity, significantly reducing controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) accidents—a leading cause of aviation fatalities.
- Traffic Collision Avoidance System (TCAS): Acts as a real-time traffic monitor to detect and warn pilots of potential mid-air collision threats, enabling evasive maneuvers well in advance.
- Autopilot and Flight Management Systems: Automated flight controls reduce pilot workload and human error during all phases of flight. Jets like the Gulfstream G650ER utilize AI-assisted autopilot features that anticipate and adjust to changing flight conditions seamlessly.
Structural and Material Innovations
Engineering advancements contribute substantially to aircraft durability and crashworthiness. The integration of carbon-fiber composites alongside traditional aluminum alloys has improved airframe strength while reducing weight, enhancing both fuel efficiency and structural resilience.
Dassault Falcon 8X and Bombardier Global 7500 prominently feature composite materials that resist fatigue and corrosion better than conventional builds. These materials enhance survivability in adverse conditions and improve longevity, reducing maintenance risks linked to structural failures.
Redundancy and Fail-Safe Design
The safest private jets incorporate multiple layers of system redundancy. Critical components such as hydraulics, electrical systems, and flight controls have backups designed to activate instantaneously upon failure of primary systems. This design philosophy ensures no single point of failure compromises flight safety.
For example, the Gulfstream G650ER is engineered with redundant avionics suites and triple hydraulic systems, allowing uninterrupted operation despite hardware malfunction.
Predictive Maintenance and Real-Time Diagnostics
Emerging technologies enable predictive maintenance through Internet of Things (IoT) sensors embedded in aircraft systems. These sensors monitor the health of engines, avionics, and structural components continuously, transmitting data to ground-based maintenance teams.
This real-time monitoring facilitates early detection of potential issues before they develop into safety hazards, minimizing unplanned downtime and preventing in-flight emergencies.
Pilot Assistance and Automation
Advances in AI and machine learning are increasingly integrated into flight decks to assist pilots with decision-making. Systems can suggest optimal flight paths, adjust for weather variations, and alert crews to anomalies that may not be immediately apparent.

These tools help mitigate human factors, which historically contribute to a significant proportion of aviation incidents. Consequently, jets equipped with these technologies, such as the Gulfstream G650ER and Bombardier Global 7500, stand out in safety rankings.
Regulatory and Industry Safety Trends Impacting Private Jet Operations
The landscape of private aviation safety is significantly shaped by evolving regulatory frameworks and industry-driven initiatives designed to enhance operational safety and accountability. For those seeking to answer “What is the safest private jet in the world?”, understanding these trends provides critical context for how safety is maintained and improved across fleets worldwide.
Regulatory Oversight and Compliance
Global aviation authorities such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) establish and enforce comprehensive safety standards that govern aircraft design, certification, pilot training, and operational procedures. These agencies require manufacturers to meet rigorous safety certification processes before private jets enter commercial service.
Over recent years, regulatory bodies have increased scrutiny on private jet operators, imposing stricter requirements on maintenance records, pilot qualifications, and operational safety audits. For example, the FAA’s Part 135 regulations for charter operations mandate enhanced safety management systems (SMS) and recurrent pilot training programs, raising the baseline safety standard industry-wide.
Industry Adoption of Safety Management Systems (SMS)
Safety Management Systems (SMS) have become an integral part of private aviation safety culture. SMS frameworks systematically identify, assess, and mitigate risks through continuous monitoring and improvement of safety practices. Progressive private jet operators increasingly integrate SMS protocols to align with commercial airline standards, significantly reducing operational risks.

Enhanced Pilot Training and Certification
The aviation industry recognizes human factors as a leading contributor to accidents. Consequently, regulatory bodies and manufacturers emphasize recurrent training, simulator sessions, and stringent certification requirements. High-end jets such as the Gulfstream G650ER often require specialized pilot training programs that exceed minimum regulatory standards, ensuring pilots are fully prepared to handle complex flight scenarios.
Transparency and Data-Driven Safety Improvements
There is a growing trend toward greater transparency in safety reporting within private aviation. Data sharing initiatives and centralized databases allow for comprehensive incident tracking and trend analysis. These data-driven insights facilitate proactive adjustments to operational procedures, helping identify emerging risks and reinforcing safety best practices.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Prioritizing Safety in Private Jet Acquisition
Selecting the safest private jet involves a strategic financial assessment beyond the aircraft’s purchase price. For business leaders and high-net-worth individuals, understanding the cost-benefit dynamics associated with safety features is essential for optimizing return on investment while ensuring operational risk mitigation.

Upfront Acquisition Costs Versus Safety Investment
Jets equipped with the most advanced safety technologies—such as the Gulfstream G650ER or Bombardier Global 7500—typically command premium purchase prices. These higher costs reflect the integration of cutting-edge avionics, robust structural materials, redundant systems, and comprehensive pilot training programs mandated by manufacturers.
While these upfront expenses may appear significant compared to entry-level models, they translate into substantial value when considering potential savings from accident avoidance, lower insurance premiums, and reduced operational disruptions.
Operating Costs Related to Safety
Ongoing operating costs are influenced by maintenance, pilot training, and technology upgrades. Aircraft with advanced safety features often require specialized maintenance, which can increase short-term expenses but reduce the likelihood of costly repairs or incidents in the long term.
Furthermore, recurrent pilot training and certification aligned with manufacturer and regulatory standards contribute to enhanced safety but add to operational budgets. Nevertheless, these investments foster a safety-first culture that mitigates human error, which is a major factor in aviation incidents.
Insurance Premiums and Risk Exposure
Insurance providers assess premiums based significantly on the safety records of aircraft models and operator compliance with safety protocols. Private jets with proven safety performance and rigorous maintenance histories, such as the Gulfstream G650ER, typically attract lower insurance costs. This reduces the total cost of ownership and offsets initial capital expenditure over the aircraft’s lifecycle.
Residual Value and Market Perception
Safety reputation directly influences the resale value of private jets. Models recognized for superior safety maintain higher residual values due to buyer confidence and lower perceived operational risks. In markets where asset liquidity is crucial, this factor offers an additional financial benefit.
Strategic ROI Considerations
From a strategic perspective, investing in the safest private jets aligns with corporate risk management objectives. Avoiding accidents not only preserves human life but also protects brand reputation, maintains uninterrupted business operations, and reduces potential legal liabilities.
Hence, the cost-benefit analysis strongly favors prioritizing safety, especially for corporate flight departments and individuals for whom security and reliability are paramount.
Comparative Overview of Leading Safe Private Jet Models
Choosing the safest private jet requires a clear understanding of how various models perform across safety, cost, and operational metrics. This section provides a comparative overview of industry-leading jets known for their safety credentials, enabling decision-makers to weigh the trade-offs efficiently. Comparative Overview of Leading Safe Private Jet Models. For a detailed guide on the best private jets overall, visit our comprehensive resource.
Comparative Table of Leading Private Jets
| Model | Gulfstream G650ER | Bombardier Global 7500 | Dassault Falcon 8X | Embraer Praetor 600 | Cessna Citation Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safety Record | Zero fatal accidents; 3M+ flight hours | Zero fatal accidents; 1M+ flight hours | Zero fatal accidents; low incidents | New, with strong safety systems | Solid safety record |
| Avionics | Symmetry Flight Deck: EGPWS, TCAS, AI-assisted automation | Vision Flight Deck: EGPWS, TCAS, advanced autopilot | EASy III Cockpit: triple-redundant systems | Advanced avionics suite | Reliable but less advanced |
| Structural Materials | Hybrid aluminum-composite frame | Carbon fiber composite airframe | Carbon fiber composite airframe | Composite-intensive structure | Traditional aluminum alloys |
| Redundancy Systems | Multiple backup hydraulics, avionics | Full critical system redundancy | Triple-redundant flight controls | Extensive redundancy | Standard redundancy |
| Acquisition Cost | $65M+ | $73M+ | $60M+ | $17M+ | $28M+ |
| Operating Costs | High due to advanced systems | High due to tech and size | Moderate | Moderate | Lower |
| Range | 7,500+ nautical miles | 7,700+ nautical miles | 6,450 nautical miles | 4,018 nautical miles | 3,500 nautical miles |
Analysis
- The Gulfstream G650ER leads with an unmatched safety record, extensive flight hours, and state-of-the-art avionics, justifying its premium cost. Learn more about the impressive speeds these jets can achieve.
- The Bombardier Global 7500 offers comparable safety with slightly higher acquisition costs but greater range.
- Dassault Falcon 8X provides a strong safety profile with robust structural design at a slightly lower price point.
- The Embraer Praetor 600 represents an emerging contender with modern safety systems and more affordable pricing.
- The Cessna Citation Longitude offers solid safety fundamentals at a more accessible cost but lacks some advanced technological features.
For operators prioritizing safety without compromising luxury and performance, the Gulfstream G650ER remains the industry benchmark. However, Bombardier and Dassault models present compelling alternatives with strong safety credentials tailored to different mission profiles and budget considerations.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
Determining what is the safest private jet in the world requires a holistic understanding of safety metrics, technology, regulatory compliance, and operational excellence. This analysis establishes the Gulfstream G650ER as the leading aircraft in safety, distinguished by its impeccable accident record, cutting-edge avionics, robust structural design, and rigorous pilot training programs. However, other models like the Bombardier Global 7500 and Dassault Falcon 8X also offer exemplary safety standards tailored to varying operational needs and budgets.
For business leaders and high-net-worth individuals, prioritizing safety is not only a matter of protecting human life but also a strategic investment that reduces financial risk, lowers insurance costs, and preserves asset value. Incorporating advanced safety technologies, maintaining strict compliance with regulatory frameworks, and fostering a culture of continuous pilot training are essential components of an effective safety strategy.
In today’s dynamic aviation environment, the safest private jets integrate predictive maintenance, AI-assisted flight systems, and redundant fail-safe designs to mitigate risks proactively. As technology evolves and regulations tighten, buyers should seek aircraft that not only meet but exceed current safety standards.
Ultimately, selecting the safest private jet demands balancing safety, cost, and operational requirements. Strategic purchasers should view safety as a critical criterion that enhances luxury travel’s reliability and peace of mind, making the Gulfstream G650ER the benchmark while considering viable alternatives aligned with their unique mission profiles.
We welcome your insights: Which private jet do you consider the safest based on your experience or research? Share your thoughts and join the conversation below. Your perspective helps shape smarter decisions in luxury aviation safety.













